 |
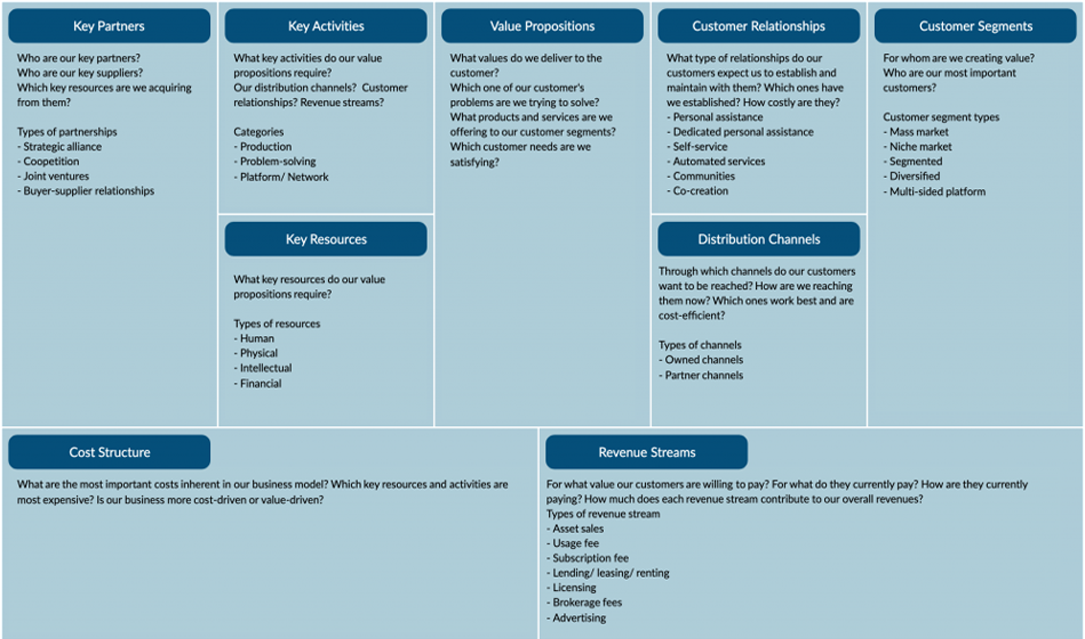
Value Proposition
The Value Proposition building block is at the heart of the business model, representing your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or value you provide for the customer segment. A value proposition should be unique and stand out from your competitors. Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design). The design of a good value proposition is an effort in itself ( see value proposition design), the results of which become this building block.
Customer Segments
Customer segments are the groups of people or companies that you are targeting to buy your product or service. Segments are based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. Segmenting gives you the opportunity to better serve needs by customizing your solution for those specific needs. Different approaches to customer segmentation include:
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. The value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Customer Relationships
This building block defines the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company. There are several types of customer relationships:
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map. It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company, and it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
Channels
This block describes how your company will communicate and transact with your customers, representing the touch points that let your customers connect with your company. Channels include how you will raise awareness of your product or service among customers, as well as how you will execute a transaction, and deliver your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to offer post-purchase support. There are two types of channels.
- Owned (direct) channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc. where the company connects directly with the customer.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc. where an independent third party connects with the customer.
Revenue Streams
Revenues streams are the sources of money and describe how you will earn revenue by providing your value proposition to your the targeted customers. A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models:
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
Different revenue sources include:
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
Key Activities
This building block defines the activities/ tasks needed to fulfill your business purpose. It includes all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work and should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue. There are 3 categories of key activities:
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
Key Resources
Key Resources describe the internal sssets required to carry out your key activities in creating and delivering your value proposition. Your resources allow your enterprise to create your offering, reach markets, maintain relationships with Customer Segments, and earn revenues. Key resources can be owned or leased by the company or acquired from key partners.
Key Partners
Key Partnerships describes the external network of suppliers and partners that provide external resources and activities needed to make the business model work. There are four different types of partnerships: strategic alliances between non-competitors, Coop-petition (strategic partnerships between competitors), Joint ventures to develop new businesses, buyer-supplier relationships to assure reliable supplies.
Cost Structure
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model. You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
|
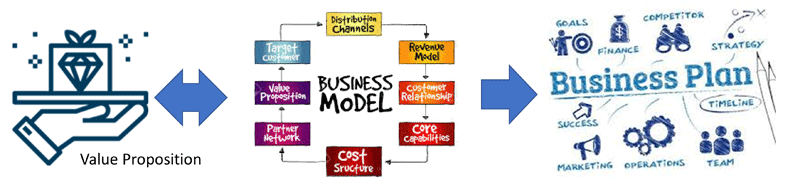






 This 3 - hour seminar presents an introduction to the concepts and components of the Business Model Canvas. It provides attendees with the foundation knowledge needed to pursue additional knowledge acquisition and use of the tools, either on their own or through additional structured training and consulting.
This 3 - hour seminar presents an introduction to the concepts and components of the Business Model Canvas. It provides attendees with the foundation knowledge needed to pursue additional knowledge acquisition and use of the tools, either on their own or through additional structured training and consulting.

 today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.
today (281.858.3271) for a free no obligation discussion of your current needs and situation.